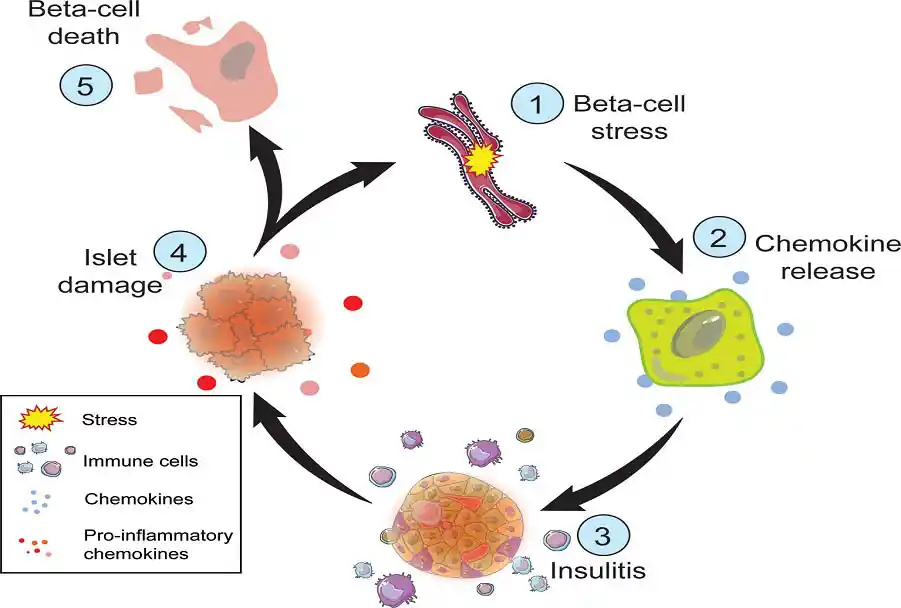
Autoimmune reactions are complex processes that occur within the body’s immune system. In these reactions, the immune system, which typically defends against harmful invaders like bacteria and viruses, mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues. One significant consequence of autoimmune reactions is their effect on beta cells in the pancreas, leading to disruptions in blood sugar regulation. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of autoimmune reactions, their impact on beta cells, and how they influence blood sugar levels.
What is an Autoimmune Reaction?
Autoimmune reactions occur when the body’s immune system, responsible for identifying and neutralizing foreign substances, begins to target its own cells and tissues. This phenomenon results from a breakdown in the immune system’s ability to distinguish between “self” and “non-self” antigens. Instead of protecting the body, the immune system launches attacks on healthy tissues, leading to inflammation, tissue damage, and various autoimmune diseases.
Impact on Beta Cells:
Beta cells are specialized cells located in the pancreas, responsible for producing insulin, a hormone crucial for regulating blood sugar levels. In autoimmune reactions, beta cells become the unfortunate targets of the immune system’s misguided assault. The immune system mistakenly recognizes beta cells as foreign invaders and launches an attack, leading to their destruction. As beta cell mass diminishes, the pancreas becomes less capable of producing insulin, resulting in insulin deficiency.
Causing Blood Sugar Fluctuations:
Beta cells, when damaged or destroyed due to autoimmune reactions, decrease insulin production, impairing glucose uptake by cells. As a result, blood sugar levels begin to rise, a condition known as hyperglycemia. This rise in blood sugar levels occurs because insulin, which plays a pivotal role in glucose metabolism by facilitating the uptake of glucose from the bloodstream into cells for energy production, is insufficiently produced.
Effects on the Body:
Persistent hyperglycemia can cause profound effects on various organ systems throughout the body. Elevated blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels, nerves, and organs, contributing to a wide range of complications associated with diabetes. These complications may include cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, nephropathy, and retinopathy, among others. Additionally, uncontrolled diabetes can increase the risk of other autoimmune diseases and infections due to compromised immune function.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
Diagnosing autoimmune reactions affecting beta cells typically involves a combination of clinical symptoms, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Blood tests measuring autoantibodies specific to beta cells, such as anti-insulin antibodies, can help confirm the presence of autoimmune diabetes. Treatment strategies aim to mitigate the immune system’s destructive effects on beta cells while managing blood sugar levels effectively.
Immunosuppressive medications may be prescribed to suppress the abnormal immune response and preserve remaining beta cell function. Additionally, insulin therapy is essential for individuals with autoimmune diabetes to compensate for the insulin deficiency and maintain optimal blood sugar control. Lifestyle modifications, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep, play crucial roles in managing blood sugar levels and supporting overall health.
Final Thoughts:
Autoimmune reactions targeting beta cells in the pancreas have significant implications for blood sugar regulation and overall health. Understanding the underlying mechanisms of autoimmune diseases and their impact on beta cell function is essential for developing effective diagnostic and treatment strategies. Through a combination of medical interventions, lifestyle modifications, and ongoing research efforts, individuals affected by autoimmune diabetes can achieve better management of their condition and improve their quality of life.
See our previous article, Bitter Bite: The Painful Impact of Junk Foods on Health, for more information on the detrimental effects of junk food on health and wellness in general.